FlyBase:ModENCODE RNA-Seq Overview
WARNING
This page has been deprecated by this newer and more up-to-date page: https://wiki.flybase.org/wiki/FlyBase:ModENCODE_data_at_FlyBase
Overview
FlyBase offers a subset of modENCODE datasets that characterize gene expression and transcriptional regulation in D. melanogaster. The modENCODE datasets incorporated by FlyBase often represent high-level distillations of data, combining or synthesizing data from multiple modENCODE experiments, rather than the raw data from individual experiments. All modENCODE datasets at FlyBase are available through JBrowse; for RNA-seq datasets, FlyBase provides additional query/analysis tools, as well as data displays on gene reports. FlyBase dataset reports provide descriptions of how data was generated and analyzed, as well as links to the original raw data at data repositories.
Please note: While FlyBase hosts a selection of tools for browsing and using modENCODE data, it is not an exhaustive resource for all data generated from the modENCODE project.
RNA-Seq Query Tools and Browsers
The primary RNA-Seq data in FlyBase are the modENCODE data originally published in Graveley et al., 2011 and Brown et al., 2014, comprising 30 developmental stage expression profiles, 29 tissue expression profiles, 25 treatment/condition expression profiles and 24 cell line expression profiles. RNA-Seq reads were mapped to the Release 6 genome assembly as described in Brown et al., 2014. In JBrowse genomic views, several other RNA-Seq datasets are also presented. The RNA-Seq query tools are restricted to the modENCODE datasets. For each modENCODE RNA-Seq sample, gene expression level was calculated as RPKM within the exonic extent of the gene, as described in Gelbart and Emmert, 2013. For purposes of presentation and queries, values were assigned to one of eight bins, from very low to extremely high.
A series of video tutorials describing different RNA-Seq tools is available. See
- RNA-Seq Part I: Using GBrowse -- Warning: The GBrowse genome viewer has been updated to JBrowse, but techniques shown here are still useful in JBrowse.
- RNA-Seq Part II: Using RNA-Seq Profile Search
- RNA Seq Part III: Searching for Similarly Expressed Genes
JBrowse
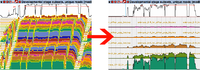
FlyBase JBrowse has several tracks that display RNA-Seq expression profiles, which give coverage values base-by-base across the genome. Choose datasets for expression by stage, tissue, treatments, or cell lines. By default, the many tracks are displayed in the layered FlyBase “TopoView” format, and data are shown on a log2 scale, since they range over many orders of magnitude. Customization options are offered to help drill down into the data, accessed by clicking on the down arrow in the track title bar.
- Space the data out. Increase the “vertical spacing between samples to prevent strong signal from one sample from obscuring the profile behind it.
- Align the profiles. Change the “Samples presentation style” from “Tilted” (default) to “Vertical” to remove the horizontal offset between adjacent RNA-Seq profiles so that they align horizontally to the same genome position.
- Choose the appropriate scaling method. Log2 scaling provides the best dynamic range for viewing both low and high signal together. Linear scaling is preferable in regions with high baseline signal, and provides a more intuitive view of the relative change in signal.
JBrowse Track Listing
JBrowse tracks sourced from modENCODE data can be enabled via the “Available Tracks” menu on the left pane of the JBrowse viewer. These tracks include:
- Genome Level Features > Transcriptional Regulatory Elements > Insulators (modENCODE, class I)
- Genome Level Features > Transcriptional Regulatory Elements > Insulators (modENCODE, class II)
- Genome Level Features > Transcriptional Regulatory Elements > Putative PREs (modENCODE)
- Transcription Factor Binding Sites (TFBS) > TFBS (modENCODE, ChIP-chip, whole embryo) > whole embryo, TFBS HOT spot analysis
- Transcription Factor Binding Sites (TFBS) > TFBS (modENCODE, ChIP-chip, whole embryo) > whole embryo, ZINC Finger TFBS
- Transcription Factor Binding Sites (TFBS) > TFBS (modENCODE, ChIP-chip, whole embryo) > whole embryo, Homeodomain TFBS
- Transcription Factor Binding Sites (TFBS) > TFBS (modENCODE, ChIP-chip, whole embryo) > whole embryo, Helix-loop-helix TFBS
- Transcription Factor Binding Sites (TFBS) > TFBS (modENCODE, ChIP-chip, whole embryo) > whole embryo, BTB/POS ChIP TFBS
- Transcription Factor Binding Sites (TFBS) > TFBS (modENCODE, ChIP-chip, whole embryo) > whole embryo, Other classes TFBS
- Transcription Factor Binding Sites (TFBS) > Other Sequence Elements > Origins of replication (modENCODE, Kc, S2, BG3 cells)
- Transcript Level Features > Transcription Start Sites (TSS) > TSS (modENCODE, embryo)
- Expression > RNA-Seq > modENCODE transcriptomes > Developmental stages
- Expression > RNA-Seq > modENCODE transcriptomes > Cell lines
- Expression > RNA-Seq > modENCODE transcriptomes > Treatments/Conditions
- Expression > RNA-Seq > modENCODE transcriptomes > Tissues > Digestive system
- Expression > RNA-Seq > modENCODE transcriptomes > Tissues > Fat body and salivary glands
- Expression > RNA-Seq > modENCODE transcriptomes > Tissues > Imaginal disc and other carcass
- Expression > RNA-Seq > modENCODE transcriptomes > Tissues > CNS and adult head
- Expression > RNA-Seq > modENCODE transcriptomes > Tissues > Gonads and male accessory glands
RNA-Seq Profile
Go to RNA-Seq Part II: Using RNA-Seq Profile Search to see the associated video tutorial.
RNA-Seq Profile is a fine grained query tool, powered by modENCODE high-throughput RNA-Seq expression data, that allows you to find genes with specific patterns of expression across several variables. Interested in development of the central nervous system? Search for genes that are expressed in these tissues during a specific developmental stage. Curious how toxins affect the fly reproductive system? Search for genes expressed in fly gonads that are activated (or suppressed) by exposure to Paraquat or Rotenone.
Choose datasets for expression by stage, tissue, treatments, or cell lines, or use several datasets in conjunction. Each dataset is presented in a form that allows you to select either narrow slices of the data, or larger sections for more coverage. You also have control over the levels of expression used in the search, allowing you to define distinct thresholds for the ON and OFF states. Keep in mind that extremely narrow search conditions may produce sparse or empty result sets. Feel free to experiment; the tool will remember your settings so that you can adjust, instead of needing to re-enter them. Search results can be exported, as usual, for further analysis or download.
NB: The group check box selectors are interpreted differently depending on whether you are making selections from the 'Expression ON' or 'Expression OFF' sections. 'Expression ON' selectors: Selecting multiple stages using one of the grouping check boxes acts as an 'OR'. This means that if a gene is expressed at or above the chosen expression level in any one or more of the selected stages it will be returned in the result list. To get 'AND' behavior (i.e., return only those genes which are expressed at the chosen level in each one of the selected stages) you must select each of the stages individually. 'Expression OFF' selectors: Selecting multiple stages using one of the grouping check boxes acts as an 'AND'. This means that for a gene to be returned in the result list, the observed level of expression must be at or below the selected level in all of the selected group stages. Therefore, for the 'expression OFF' selectors, checking a group check box is functionally identical to selecting each individual sub-category.
RNA-Seq Similarity
Go to RNA Seq Part III: Searching for Similarly Expressed Genes to see the associated video tutorial.
RNA-Seq Similarity finds genes with expression patterns that are similar to that of a given gene; this search option can also be launched from the relevant gene page. 'Similar to' in this case means that the pattern of higher and lower expression1 in the categories for the RNA-Seq expression experiment data you choose are close to those of your chosen gene, as measured by the correlation coefficient2 between the data for your given gene and each of the search result genes. Enter your query gene symbol in the box, and choose to search for genes with similar expression by developmental stage, tissue, treatments, or cell lines. You can also specify a subset of experimental samples within a set of RNA-Seq expression data to use when making comparisons. The resulting genes can be exported to a FlyBase hit list.
1 Note that two expression patterns will be flagged as similar if the profile of peaks and troughs of expression have a similar shape, even though one expression pattern may have much higher or lower values overall.
2 FlyBase uses a generalized Spearman rank correlation for this statistic.
RNA-Seq By Region
RNA-Seq By Region can be used to compare the RNA-Seq signal for a given region across samples, or to compare signal between two regions within a single sample.
Supply the symbol or FBgn ID for one gene of interest, and choose to query either the developmental or tissue RNA-Seq profiles. The tool will retrieve the locations of all exons for the gene specified, and report an average RNA-Seq signal for each region. Values are normalized for read depth across a given set, and reported as values from 1 to 50; very high read values are truncated at a value of 50. Alternatively, input one or more genomic regions using standard JBrowse coordinate nomenclature (e.g., X:350000..351000) and the tool will return the average RNA-Seq signal for each submitted genomic span; for multiple regions, enter one region per line in the input box.
For fast visual inspection of the potentially large expression tables, the background of table cells is colored in the same way as in the heatmap coloring schema of expression histograms in FlyBase gene reports. These tables can be copied and downloaded and used for further analysis.
Note that the signal reported for a given region may arise from the expression of multiple transcripts from one or more genes; the tool simply reports the total signal for that region and does not attempt to assign the expression in that region to any specific transcript.