Difference between revisions of "FlyBase:GBrowse Tracks"
m |
|||
| (79 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | == Reference Genome Annotations [http:// | + | |
| + | {| class="wikitable" style="text-align: center; color: red; margin: auto;" | ||
| + | !colspan="1"|Warning | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |rowspan="1"|Information about GBrowse is only relevant to users of an [http://flybase.org/downloads/archivedata archived] instance of FlyBase earlier than FB2022_05. | ||
| + | For users working with the current release at [http://flybase.org/ flybase.org], please see our page about [[FlyBase:JBrowse]], the genome viewer that replaced GBrowse. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Updated 21 December 2017 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Below is a detailed list of tracks available on the D. melanogaster GBrowse viewer. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Reference Genome Annotations [http://flybase.org/reports/FBsn0000272.html (iso-1)] == | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Note:''' The genome release is shown in the top right corner of the screen, e.g. ''D. melanogaster'' (R6.07). The number before the decimal refers to the version of the genome sequence, currently, Release 6 (R6) [http://flybase.org/reports/FBrf0227719.html (Hoskins et al, 2015)], which does not change between major releases. The number after the decimal point refers to the version of the annotation set, which may be updated at each release. The ''D. melanogaster'' gene set consists of gene models manually annotated by FlyBase annotators (with the exception of some classes of small non-coding RNAs) (Matthews, et al., (2015). G3 (Bethesda) 5(5):777-801). | ||
'''Gene Span''' Shows the total extent of the transcribed region of an annotated gene (including non-coding genes), with direction of transcription indicated. No transcript substructure is shown; corresponds to the entire extent defined by all annotated transcripts. Hyperlinked to Gene Report; label shows FlyBase gene symbol. | '''Gene Span''' Shows the total extent of the transcribed region of an annotated gene (including non-coding genes), with direction of transcription indicated. No transcript substructure is shown; corresponds to the entire extent defined by all annotated transcripts. Hyperlinked to Gene Report; label shows FlyBase gene symbol. | ||
| − | '''Transcript''' [http://{{ | + | '''Transcript''' [http://{{flybaseorg}}/cgi-bin/cvreport.pl?rel=is_a&id=SO:0000673 SO:0000673] Shows the exon (wider bars) and intron (black line) structure of each annotated coding transcript, with direction of transcription indicated. Hyperlinked Transcript Report; if label option is on, shows FlyBase symbol. |
'''CDS''' Shows extent of sequence encoding each specific polypeptide, with direction of transcription indicated; introns indicated as narrow lines. Hyperlinked to Polypeptide Report; if label option is on, shows FlyBase symbol. | '''CDS''' Shows extent of sequence encoding each specific polypeptide, with direction of transcription indicated; introns indicated as narrow lines. Hyperlinked to Polypeptide Report; if label option is on, shows FlyBase symbol. | ||
| − | '''Natural TE''' [http://{{ | + | '''Natural TE''' [http://{{flybaseorg}}/cgi-bin/cvreport.pl?rel=is_a&id=SO:0000101 SO:0000101] Shows the extent of a natural transposable element in the sequenced strain (at the time it was sequenced). Hyperlinked to Natural Transposon report; if label option is on, shows FlyBase symbol. |
| − | '''Repeat region''' Regions of genomic repeats and low complexity DNA sequences, as computed using RepeatMasker and RepeatRunner [http://{{ | + | '''Repeat region''' Regions of genomic repeats and low complexity DNA sequences, as computed using RepeatMasker and RepeatRunner [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBrf0194515.html (Smith, et al., 2007)]. |
== General == | == General == | ||
| − | '''Estimated Cytological band''' Approximate extent of the classical cytological chromosome bands described by Bridges. See [http://{{ | + | '''Estimated Cytological band''' Approximate extent of the classical cytological chromosome bands described by Bridges. See [http://{{flybaseorg}}/wiki/FlyBase:Computed_cytological_data Computed cytological data] in FlyBase for a detailed description of how this computed cytological location is calculated. See [http://{{flybaseorg}}/wiki/FlyBase:Maps FlyBase Maps] for a collection of polytene chromosome images. |
'''3-frame translation (forward)''' If zoomed out (greater than 400bp), shows ticks at sites of stop codons for the three frames on the forward strand. If zoomed in (400bp or less), shows predicted translations for each frame, using single-letter amino acid code. | '''3-frame translation (forward)''' If zoomed out (greater than 400bp), shows ticks at sites of stop codons for the three frames on the forward strand. If zoomed in (400bp or less), shows predicted translations for each frame, using single-letter amino acid code. | ||
| Line 23: | Line 38: | ||
== Aligned Evidence == | == Aligned Evidence == | ||
| − | '''cDNA''' D. melanogaster cDNA sequences submitted to the sequence databases; shows the exon (wider bars) and intron (black line) structure, and direction of transcription. Sequences | + | '''cDNA''' D. melanogaster cDNA sequences from large-scale submissions submitted to the sequence databases; shows the exon (wider bars) and intron (black line) structure, and direction of transcription. Sequences are aligned to release 6 by NCBI and submitted to FlyBase. Some genomic DNA submissions, including third party submissions, are included in this tier. |
| + | |||
| + | '''EST''' ("expressed sequence tag") Indicated in light green. Partial sequence of a cDNA; shows the exon (wider bars) and intron (narrow bars) structure, and direction of transcription. Sequences are aligned to release 6 by NCBI and submitted to FlyBase. | ||
| − | ''' | + | '''other aligned sequences''' D. melanogaster aligned nucleotides submitted to the sequence databases. Sequences are aligned to release 6 by NCBI and submitted to FlyBase. Some genomic DNA submissions, including third party submissions, are included in this tier. |
| − | ''' | + | '''RNA-Seq based exon junctions''' Indicated in blue. Orientation of the junction is indicated by an arrowhead in the center of the junction. Mousing over the glyph for a RNA-Seq junction activates a pop-up indicating the total read counts for the junction. The read counts are separated based upon which dataset the information is from (modENCODE or Baylor, see below for Dataset Report links). |
| − | + | See the [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000204.html BCM_1_RNAseq_junctions] and [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000203.html modENCODE_mRNA-Seq_U_junctions] Dataset Reports. | |
| − | ''' | + | '''PeptideAtlas peptides''' Indicated in yellow. Alignment of peptide sequences determined by mass spectroscopy, derived from polypeptides isolated from the sequenced strain at various developmental stages. Contributed by the Center for Model Organism Proteomes, SystemsX and Research Priority Project of the University of Zurich, Switzerland. For more information, see [https://db.systemsbiology.net/sbeams/cgi/PeptideAtlas/buildDetails?atlas_build_id=352 Peptide Atlas] |
| − | ''' | + | '''Transcription Start Sites (modENCODE), embryo''' Transcription start site (TSS) regions identified by integrative analysis of ESTs, CAGE or RLM-RACE, modENCODE. The horizontal extent of the blue arrow indicates the range over which 90 percent of the TSS signal is located. The red bars indicate TSS usage at single base resolution along the genome. Clicking on the TSS feature will link to the relevant Sequence Feature report. Note: data for embryonic stages only. See the [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000202.html mE_Transcription_Start_Sites] Dataset Report. |
| + | |||
| + | '''Transcription Start Sites (RAMPAGE), peak calls''' Transcription start site regions (peak calls) identified by RAMPAGE-Seq across 36 stages of development, depicted as green arrow glyphs. The arrow points in the direction of transcription. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Transcription Start Sites (RAMPAGE), early embryo 0-12hr, stranded RNA-Seq''' Profile of capped transcript 5' ends observed by RAMPAGE-Seq for 12 stages of early embryogenesis. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Transcription Start Sites (RAMPAGE), late embryo 13-24hr, stranded RNA-Seq''' Profile of capped transcript 5' ends observed by RAMPAGE-Seq for 12 stages of late embryogenesis. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Transcription Start Sites (RAMPAGE), larva/pupa/adult, stranded RNA-Seq''' Profile of capped transcript 5' ends observed by RAMPAGE-Seq for 12 larval, pupal or adult stages. | ||
| + | |||
| + | See the [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000537.html TSS_'''RAMPAGE] Dataset Report. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Transcription Start Sites (MachiBase), stranded RNA-Seq''' Profile of capped transcript 5' ends observed by MachiBase CAGE-Seq for embryonic, larval, adult male and female (young or old) and S2 cell line samples. | ||
| + | See the [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000725 TSS_MachiBase] Dataset Report. | ||
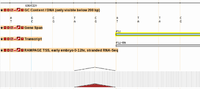
| − | [ | + | [[File:TopoViewOneOff.png|200px|right|Known bug.]] |
| − | + | Please note that the signal shown for the Transcription Start Site data (RAMPAGE and MachiBase) is one base off: i.e., the signal is shown one base to the left of where it should be. In the example to the right, the signal should map to the first base (3R:6864324, A) of the ftz transcript, but is instead shown one base to the left (3R:6864323, C). This is a known bug and we're working to fix this. | |
| − | ''' | + | '''Protein domains (PFAM)''' [http://pfam.xfam.org/ Pfam] protein domains identified in annotated proteins, as obtained from [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/download.html InterPro], are mapped to the genome. |
| − | ''' | + | '''Protein domains (SMART)''' [http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/ SMART] protein domains identified in annotated proteins are mapped to the genome. |
| − | [http://{{ | + | '''RNA Editing Sites''' A-to-I RNA editing sites.<br /> |
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000259 mE_A-to-I_RNA_Editing_Sites] Dataset Report. <br /> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000519 Rosbash_Adult_Head_A-to-I_Editing_Sites] Dataset Report. <br /> | ||
== Mapped Mutations == | == Mapped Mutations == | ||
| − | '''Transgene insertion site''' [http://{{ | + | '''Transgene insertion site''' [http://{{flybaseorg}}/cgi-bin/cvreport.pl?rel=is_a&id=SO:0000368 SO:0000368] Thin rectangles indicate the site of transposon insertion. If the estimated insertion range is larger than 10 nucleotides, there are short dashes on either side of the rectangle. In those cases, see the Insertion Report for more information about localization. If known, the orientation of the transposon (relative to that transposon's inherent asymmetry) is indicated by an arrow (pointing 5'-to-3'). To determine the orientation of functional elements within a transposon (e.g., FRT, UAS, etc.), consult the FlyBase construct reports, as described in this [[Media:InsertionOrientation.pdf|guide]]. |
| − | '''Transgenic insertions in stocks, Bloomington''' [http://{{ | + | '''Transgenic insertions in stocks, Bloomington''' [http://{{flybaseorg}}/cgi-bin/cvreport.pl?rel=is_a&id=SO:0000368 SO:0000368] This track functions just as the "Transgenic Insertion Site" track described above. This track contains only insertions available from the Bloomington Stock Center. Links to the relevant Stock Report can be found at the bottom of the Insertion Report, which is linked from the feature glyph. |
| − | '''Transgenic insertions in stocks, Kyoto''' [http://{{ | + | '''Transgenic insertions in stocks, Kyoto''' [http://{{flybaseorg}}/cgi-bin/cvreport.pl?rel=is_a&id=SO:0000368 SO:0000368] This track functions just as the "Transgenic Insertion Site" track described above. This track contains only insertions available from the Kyoto Stock Center. Links to the relevant Stock Report can be found at the bottom of the Insertion Report, which is linked from the feature glyph. |
| − | '''Transgenic insertions in stocks, Harvard''' [http://{{ | + | '''Transgenic insertions in stocks, Harvard''' [http://{{flybaseorg}}/cgi-bin/cvreport.pl?rel=is_a&id=SO:0000368 SO:0000368] This track functions just as the "Transgenic Insertion Site" track described above. This track contains only insertions available from the Harvard Medical School Stock Center. Links to the relevant Stock Report can be found at the bottom of the Insertion Report, which is linked from the feature glyph. |
| − | '''Point mutation''' [http://{{ | + | '''Point mutation''' [http://{{flybaseorg}}/cgi-bin/cvreport.pl?rel=is_a&id=SO:1000008 SO:1000008] A single nucleotide has been changed into another nucleotide. Location of mutation is indicated with a grey bar and labeled with the FlyBase allele symbol. The feature glyph is linked to the related Allele Report. |
| − | '''Sequence variant''' [http://{{ | + | '''Sequence variant''' [http://{{flybaseorg}}/cgi-bin/cvreport.pl?rel=is_a&id=SO:0000109 SO:0000109] A region of sequence where variation has been observed. Often these refer to natural variants of a protein that lead to two different functions. The location of the mutation is indicated with a grey bar and labeled with the FlyBase allele symbol. The feature glyph is linked to the related Allele Report. |
| − | '''Uncharacterized change in nucleotide sequence''' [http://{{ | + | '''Uncharacterized change in nucleotide sequence''' [http://{{flybaseorg}}/cgi-bin/cvreport.pl?rel=is_a&id=SO:1000007 SO:1000007] The nature of the nucleotide substitution is either uncharacterized or only partially characterized. The location of the mutation is indicated with grey bar and labeled with the FlyBase allele symbol. The feature glyph is linked to the related Allele Report. |
| − | '''Aberration junction''' [http://{{ | + | '''Aberration junction''' [http://{{flybaseorg}}/cgi-bin/cvreport.pl?rel=is_a&id=SO:0000687 SO:0000687] Location of aberration breakpoint reported in the literature. Labeled with FlyBase aberration symbol designation and the numerical designation of the breakpoint mapped (where known). Often the exact breakpoint location is unknown and the feature indicates a range within which the breakpoint has been mapped. Genetic data is available in the Aberration Report which can be accessed directly by clicking on the feature. |
| − | '''Complex substitution''' [http://{{ | + | '''Complex substitution''' [http://{{flybaseorg}}/cgi-bin/cvreport.pl?rel=is_a&id=SO:1000005 SO:1000005] The mutation does not fall simply into any of the other categories and is often a combination of events, e.g. deletion of 20 bases and insertion of 11 unrelated bases. Location of mutation is indicated with a grey bar and labeled with the FlyBase allele symbol. Feature is linked to the related Allele Report. |
| − | ''' | + | '''Indel''' [http://{{flybaseorg}}/cgi-bin/cvreport.pl?rel=is_a&id=SO:1000032 SO:1000032] The junction where an insertion or deletion of one or more nucleotides occurred. Location of mutation is indicated with a grey bar and labeled with the FlyBase allele symbol. In the case of deletions, the extent of the deletion is indicated by a grey bar. In the case of nucleotide insertions, the location of the nucleotide(s) insertion is indicated by a vertical grey line. Features are linked to the related Allele Report. |
| − | '''Rescue fragment''' [http://{{ | + | '''Rescue fragment''' [http://{{flybaseorg}}/cgi-bin/cvreport.pl?rel=is_a&id=SO:0000411 SO:0000411] Locations of transgenic rescue fragment reported in the literature. Labeled with FlyBase allele symbol designation. Features are linked to the related Allele Reports which contain genetic data. |
== Gene Predictions == | == Gene Predictions == | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
'''NCBI gnomon, 2006''' (coding region of transcript) generated via a hidden Markov model using transcript alignment constraints and protein hit information, if available; allows prediction of alternatively spliced isoforms (Souvorov, et al., 2006, NCBI); submitted by J. Ostell. | '''NCBI gnomon, 2006''' (coding region of transcript) generated via a hidden Markov model using transcript alignment constraints and protein hit information, if available; allows prediction of alternatively spliced isoforms (Souvorov, et al., 2006, NCBI); submitted by J. Ostell. | ||
| Line 75: | Line 105: | ||
'''CONTRAST''' (coding region of transcript) using a semi-Markov conditional random field (Gross, Do, and Batzoglou, 2005, BCATS 2005 Symposium Proceedings, p. 82); submitted by S. Batzoglou. | '''CONTRAST''' (coding region of transcript) using a semi-Markov conditional random field (Gross, Do, and Batzoglou, 2005, BCATS 2005 Symposium Proceedings, p. 82); submitted by S. Batzoglou. | ||
| − | '''PhyloCSF (CONGO)''' Exon prediction. Region of sequence conservation across multiple Drosophila species, with a pattern of conservation indicative of a protein-coding extent and termini consistent with exon structure (start, splice or stop); submitted by M. Lin and M. Kellis. Related publications: [http://{{ | + | '''PhyloCSF (CONGO)''' Exon prediction. Region of sequence conservation across multiple Drosophila species, with a pattern of conservation indicative of a protein-coding extent and termini consistent with exon structure (start, splice or stop); submitted by M. Lin and M. Kellis. Related publications: [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBrf0202906.html Lin MF, Carlson, JW et al. (2007)], [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBrf0213957.html Lin MF, Jungreis I, and Kellis M. (2011)] |
== Similarity== | == Similarity== | ||
| Line 81: | Line 111: | ||
=== Proteins (aligned by BLAST) === | === Proteins (aligned by BLAST) === | ||
| − | '''Dmel proteins''' D. melanogaster protein sequences submitted to the sequence databases. | + | '''Dmel proteins''' D. melanogaster protein sequences submitted to the sequence databases. Proteins are aligned to release 6 by NCBI and submitted to FlyBase. |
| − | '''Other proteins''' Protein sequences submitted to the sequence databases since 2003, from species other than D. melanogaster; aligned | + | '''Other proteins''' Protein sequences submitted to the sequence databases since 2003, from species other than D. melanogaster; Proteins are aligned to release 6 by NCBI and submitted to FlyBase. |
=== Synteny Features === | === Synteny Features === | ||
| Line 91: | Line 121: | ||
== Noncoding Features == | == Noncoding Features == | ||
| − | '''Insulators class I''' [http://{{ | + | '''Insulators (modENCODE, class I)''' [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000058.html Insulator_Class_I.mE01] Dataset Report |
| − | '''Insulators class II''' [http://{{ | + | '''Insulators (modENCODE, class II)''' [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000059.html Insulator_Class_II.mE01 ] Dataset Report |
| − | ''' | + | '''TFBS (EMSA, footprinting)'''. Indicated by grey bar. Locations of protein binding sites reported in the literature, as compiled by FlyBase and/or [http://redfly.ccr.buffalo.edu/ REDfly]). Reference and supporting information available on related Sequence Feature reports (click feature glyph to access report). See also the [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000494.html REDfly TFBSs] dataset report. |
| − | ''' | + | '''Putative PREs (modENCODE)''' [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000414.html mE1_HDAC_PRE ] Dataset Report. Genomic sequences identified as putative polycomb response elements (silencers) in embryos. |
| − | ''' | + | '''Transcriptional Regulatory Regions (REDfly)'''. Indicated by grey bar. Locations of regulatory regions reported in the literature, as compiled by FlyBase and/or [http://redfly.ccr.buffalo.edu/ REDfly]). Reference and supporting information available on related Sequence Feature reports (click feature glyph to access report). See also the [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000493.html REDfly CRMs] dataset report. |
| − | ''' | + | '''ChIP (whole embryo) – TF HOT spot analysis''' [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000258.html mE1_TFBS_HSA ] Dataset Report. Genomic sequences identified as unique regions of transcription factor (TF) binding using HOT spot analysis (HSA); one or many TFs may bind in a given region. A synthesis of ChIP data sets for 41 different transcription factors. TF binding profiles used in this analysis were assayed at early embryo stages. Mousing over the feature pops up a box that lists the transcription factor genes that bind within the region. Clicking on the feature links to the related Sequence Feature report. |
| − | ''' | + | '''ChIP (whole embryo) – zinc finger TFs''' Binding sites for transcriptions factors that contain one or more zinc finger domains. Clicking on the feature links to the related Sequence Feature report. The following Dataset Reports comprise the data found in this track. |
| − | + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000293.html mE1_TFBS_disco]<br /> | |
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000299.html mE1_TFBS_ftz-f1]<br /> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000300.html mE1_TFBS_GATAe]<br /> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000303.html BDTNP1_TFBS_hb]<br /> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000304.html mE1_TFBS_hkb]<br /> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000308.html BDTNP1_TFBS_kni]<br /> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000309.html mE1_TFBS_Kr]<br /> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000314.html mE1_TFBS_sbb]<br /> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000315.html mE1_TFBS_sens]<br /> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000316.html BDTNP1_TFBS_shn]<br /> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000318.html BDTNP1_TFBS_sna]<br /> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000320.html BDTNP1_TFBS_tll]<br /> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000326.html mE1_TFBS_zfh1]<br /> | ||
| − | + | '''ChIP (whole embryo) – homeodomain TFs''' Binding sites for transcriptions factors that contain one or more homeodomains. The following Dataset Reports comprise the data found in this track. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000287.html BDTNP1_TFBS_bcd] <br /> | |
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000288.html mE1_TFBS_cad] <br /> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000295.html mE1_TFBS_Dll] <br /> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000296.html mE1_TFBS_en] <br /> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000297.html mE1_TFBS_eve] <br /> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000298.html BDTNP1_TFBS_ftz] <br /> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000305.html mE1_TFBS_inv] <br /> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000312.html BDTNP1_TFBS_prd] <br /> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000324.html mE1_TFBS_Ubx] <br /> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000325.html BDTNP1_TFBS_z] <br /> | ||
| − | + | '''ChIP (whole embryo) – helix-loop-helix TFs''' Binding sites for transcriptions factors that contain one or more helix-loop-helix domains. The following Dataset Reports comprise the data found in this track. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000292.html BDTNP1_TFBS_da ] <br /> | |
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000302.html mE1_TFBS_h ] <br /> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000307.html mE1_TFBS_kn ] <br /> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000323.html BDTNP1_TFBS_twi ] <br /> | ||
| − | + | '''ChIP (whole embryo) – BTB/POZ TFs''' Binding sites for transcriptions factors that contain one or more BTB/POZ domains. The following Dataset Reports comprise the data found in this track. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000286.html mE1_TFBS_bab1 ] <br /> | |
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000289.html mE1_TFBS_chinmo ] <br /> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000321.html mE1_TFBS_Trl ] <br /> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000322.html mE1_TFBS_ttk ] <br /> | ||
| − | + | '''ChIP (whole embryo) – other TFs''' Binding sites for transcriptions factors that do not fall into one of the other categories. The following Dataset Reports comprise the data found in this track. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000290.html mE1_TFBS_cnc ] <br /> | |
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000291.html mE1_TFBS_D ] <br /> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000294.html BDTNP1_TFBS_dl ] <br /> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000301.html BDTNP1_TFBS_gt ] <br /> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000306.html mE1_TFBS_jumu ] <br /> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000310.html BDTNP1_TFBS_Mad ] <br /> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000311.html BDTNP1_TFBS_Med ] <br /> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000313.html mE1_TFBS_run ] <br /> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000317.html BDTNP1_TFBS_slp1 ] <br /> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000319.html mE1_TFBS_Stat92E ] <br /> | ||
| − | [ | + | '''ChIP (mesoderm) - various TFs''' ChIP-chip binding peak calls for 13 TFs that control mesodermal development at various points of embryogenesis. There are 28 samples in all, displayed as distinct subtracks (use the [[FlyBase:GBrowse#Customizing_subtrack_display|subtrack selection menu]] to turn subtracks on/off and reorder them). These data were kindly provided by Eileen Furlong's lab (EMBL), comprising several studies: [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBrf0209262.html Zinzen et al., 2009], [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBrf0217348.html Bonn et al., 2012], [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBrf0217404.html Junion et al., 2012], [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBrf0223915.html Rembold et al., 2014] and [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBrf0225471.html Ciglar et al., 2014]. These 28 ChIP-chip datasets were processed in parallel by Matthias Monfort of the Furlong group, as described [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBrf0227761.html here]. More details on each subtrack are available in the FlyBase dataset reports, with links to the appropriate data repository. |
| − | [http://{{ | ||
| − | [http://{{ | ||
| − | [http://{{ | ||
| − | [http://{{ | ||
| − | [http://{{ | ||
| − | |||
| − | [http://{{ | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000680.html ChIP-chip_bap_E6-8h_organism] <br/> | |
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000681.html ChIP-chip_bin_E6-8h_organism] <br/> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000682.html ChIP-chip_bin_E8-10h_organism] <br/> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000683.html ChIP-chip_bin_E10-12h_organism] <br/> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000684.html ChIP-chip_Doc2_E4-6h_organism] <br/> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000685.html ChIP-chip_Doc2_E6-8h_organism] <br/> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000688.html ChIP-chip_lmd_E6-8h_organism] <br/> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000696.html ChIP-chip_pMad_E4-6h_organism] <br/> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000697.html ChIP-chip_pMad_E6-8h_organism] <br/> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000689.html ChIP-chip_Mef2_E2-4h_organism] <br/> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000690.html ChIP-chip_Mef2_E4-6h_organism] <br/> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000691.html ChIP-chip_Mef2_E6-8h_organism] <br/> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000692.html ChIP-chip_Mef2_E8-10h_organism] <br/> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000693.html ChIP-chip_Mef2_E10-12h_organism] <br/> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000686.html ChIP-chip_pan_E4-6h_organism] <br/> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000687.html ChIP-chip_pan_E6-8h_organism] <br/> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000694.html ChIP-chip_pnr_E4-6h_organism] <br/> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000695.html ChIP-chip_pnr_E6-8h_organism] <br/> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000698.html ChIP-chip_slp1_E4-6h_organism] <br/> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000699.html ChIP-chip_slp1_E6-8h_organism] <br/> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000700.html ChIP-chip_sna_E2-4h_organism] <br/> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000701.html ChIP-chip_tin_E2-4h_organism] <br/> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000702.html ChIP-chip_tin_E4-6h_organism] <br/> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000703.html ChIP-chip_tin_E6-8h_organism] <br/> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000704.html ChIP-chip_ttk_E6-8h_organism] <br/> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000705.html ChIP-chip_twi_E2-4h_organism] <br/> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000706.html ChIP-chip_twi_E4-6h_organism] <br/> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000707.html ChIP-chip_twi_E6-8h_organism] <br/> | ||
| − | ''' | + | '''ChIP (mesoderm) - His3 modifications''' Peak calls for ChIP-seq of histone modifications obtained from purified embryonic mesodermal nuclei. Data are available for H3K4me1, H3K4me3, H3K27Ac, H3K27me3, H3K36me3, H3K79me3 and RNA Pol II, displayed as 7 distinct [[FlyBase:GBrowse#Customizing_subtrack_display|subtracks]]. Data were kindly provided by Eileen Furlong's lab (EMBL), as published in [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBrf0217348.html Bonn et al., 2012]. Data analysis methods by Matthias Monfort (of the Furlong group) are described [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBrf0227761.html here]. More details on each subtrack are available in the FlyBase dataset reports, with links to the appropriate data repository. |
| − | + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000710.html ChIP-seq_H3K4me1_E6-8h_mesoderm] <br/> | |
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000715.html ChIP-seq_H3K27Ac_E6-8h_mesoderm] <br/> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000711.html ChIP-seq_H3K4me3_E6-8h_mesoderm] <br/> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000709.html ChIP-seq_RpII33_E6-8h_mesoderm] <br/> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000713.html ChIP-seq_H3K79me3_E6-8h_mesoderm] <br/> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000714.html ChIP-seq_H3K36me3_E6-8h_mesoderm] <br/> | ||
| + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000712.html ChIP-seq_H3K27me3_E6-8h_mesoderm] <br/> | ||
| − | ''' | + | '''Chromatin domains''' 5-state model, Kc cells [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000187.html Chromatin_types_NKI.Kc167 ] Dataset Report. Whole-genome DamID binding profiles of 53 chromatin proteins in Drosophila Kc167 cells were generated and/or analyzed. In the same array platform, ChIP-on-chip profiles of histone H3, H1, H3K9me2, H3K27me3, H3K4me2, and H3K79me3 were obtained. These were correlated with gene expression, which was measured by RNA-tag profiling.<br /> |
| − | ''' | + | '''Chromatin domains''' 9-state model, S2 cells [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000199.html Chromatin_types_mE1.S2 ] Dataset Report. Demarcation of chromatin domains of nine major types based on analysis of 18 histone modification profiles.<br /> |
| − | [http://{{ | + | |
| − | [http://{{ | + | '''Chromatin domains''' 9-state model, BG3 cells [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000200.html Chromatin_types_mE2.BG3 ] Dataset Report. Demarcation of chromatin domains of nine major types based on analysis of 18 histone modification profiles.<br /> |
| + | |||
| + | '''Origins of replication''' [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000188.html mE_Early_Replication_Origins_cells] and [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000189.html mE_Orc2_ChIP-Seq_cells] Dataset Reports. Genome profile of early activating origins of replication, based on BrdU label or Orc2 binding, characterized in Kc167, ML-DmBG3-c2 and S2-DRSC cell lines. <br /> | ||
==Microarray Features== | ==Microarray Features== | ||
| − | '''Affymetric v1''' [http://{{ | + | '''Affymetric v1''' [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000327.html Affymetrix_GeneChip_v1 ] Dataset Report. Oligonucleotides (25-mers) designed by Affymetrix to correspond to annotated transcripts in D. melanogaster. Used for the Affymetrix GeneChip Drosophila Genome Array DrosGenome1 microarray, release date February 19, 2002. |
| − | '''Affymetric v2''' [http://{{ | + | '''Affymetric v2''' [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000029.html Affymetrix_GeneChip_v2 ] Dataset Report. Oligonucleotides (25-mers) designed by Affymetrix to correspond to annotated transcripts in D. melanogaster. Used for the Affymetrix GeneChip Drosophila Genome 2.0 Array, release date July 1, 2004. |
| − | '''DGRC-1 amplicons''' [http://{{ | + | '''DGRC-1 amplicons''' [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000027.html DGRC-1] Dataset Report. Indicated in orange. DNA fragments amplified from D. melanogaster genomic DNA (OregonR) by the [https://dgrc.bio.indiana.edu/Home Drosophila Genomics Resource Center (DGRC)], using gene-specific primers made by [http://www.incyte.com/ Incyte] and designed to target transcribed regions with minimal sequence similarity to other genes. Used for the DGRC-D.melanogaster-DGRC1-15552-v5 amplicon microarray, release date June 2, 2006 (original release of v1, May 2004) . For further information see the DGRC-1 library collection report. |
| − | '''DGRC-2 oligos''' [http://{{ | + | '''DGRC-2 oligos''' [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000028.html DGRC-2] Dataset Report. Indicated in orange. "Long oligos" (65-69mers) designed to correspond to annotated transcripts in D. melanogaster (r4.3); synthesized by [http://www.flychip.org.uk/ FlyChip] in collaboration with the International Drosophila Array Consortium INDAC and the [https://dgrc.bio.indiana.edu/Home Drosophila Genomics Resource Center (DGRC)]. Used for the DGRC-D.melanogaster-DGRC2-17328-v1 oligonucleotide microarray, release date June 20,2006. For further information see the DGRC-2 library collection report. |
==Expression Levels== | ==Expression Levels== | ||
| Line 189: | Line 254: | ||
'''Digestive system''' <br /> | '''Digestive system''' <br /> | ||
| − | [http://{{ | + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000227.html mE_mRNA_L3_Wand_dig_sys]<br /> |
| − | [http://{{ | + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000219.html mE_mRNA_A_1d_dig_sys] <br /> |
| − | [http://{{ | + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000223.html mE_mRNA_A_4d_dig_sys] <br /> |
| − | [http://{{ | + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000221.html mE_mRNA_A_20d_dig_sys] <br /> |
'''Fat body and salivary glands''' <br /> | '''Fat body and salivary glands''' <br /> | ||
| − | [http://{{ | + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000228.html mE_mRNA_L3_Wand_fat] <br /> |
| − | [http://{{ | + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000233.html mE_mRNA_WPP_fat] <br /> |
| − | [http://{{ | + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000235.html mE_mRNA_P8_fat] <br /> |
| − | [http://{{ | + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000230.html mE_mRNA_L3_Wand_saliv]<br /> |
| − | [http://{{ | + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000234.html mE_mRNA_WPP_saliv] <br /> |
'''Imaginal disc and other carcass''' <br /> | '''Imaginal disc and other carcass''' <br /> | ||
| − | [http://{{ | + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000229.html mE_mRNA_L3_Wand_imag_disc] <br /> |
| − | [http://{{ | + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000226.html mE_mRNA_L3_Wand_carcass] <br /> |
| − | [http://{{ | + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000218.html mE_mRNA_A_1d_carcass] <br /> |
| − | [http://{{ | + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000222.html mE_mRNA_A_4d_carcass] <br /> |
| − | [http://{{ | + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000220.html mE_mRNA_A_20d_carcass] <br /> |
'''CNS and adult head''' <br /> | '''CNS and adult head''' <br /> | ||
| − | [http://{{ | + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000225.html mE_mRNA_L3_CNS] <br /> |
| − | [http://{{ | + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000224.html mE_mRNA_P8_CNS] <br /> |
| − | [http://{{ | + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000209.html mE_mRNA_A_MateM_1d_head] <br /> |
| − | [http://{{ | + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000216.html mE_mRNA_A_MateM_4d_head] <br /> |
| − | [http://{{ | + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000214.html mE_mRNA_A_MateM_20d_head] <br /> |
| − | [http://{{ | + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000210.html mE_mRNA_A_VirF_1d_head] <br /> |
| − | [http://{{ | + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000211.html mE_mRNA_A_VirF_4d_head] <br /> |
| − | [http://{{ | + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000231.html mE_mRNA_A_VirF_20d_head] <br /> |
| − | [http://{{ | + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000207.html mE_mRNA_A_MateF_1d_head] <br /> |
| − | [http://{{ | + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000213.html mE_mRNA_A_MateF_4d_head] <br /> |
| − | [http://{{ | + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000212.html mE_mRNA_A_MateF_20d_head] <br /> |
'''Gonads and male accessory glands'''<br /> | '''Gonads and male accessory glands'''<br /> | ||
| − | [http://{{ | + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000217.html mE_mRNA_A_MateM_4d_testis] <br /> |
| − | [http://{{ | + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000215.html mE_mRNA_A_MateM_4d_acc_gland] <br /> |
| − | [http://{{ | + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000232.html mE_mRNA_A_VirF_4d_ovary] <br /> |
| − | [http://{{ | + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000208.html mE_mRNA_A_MateF_4d_ovary]<br /> |
'''L3 CNS neuron'''<br /> | '''L3 CNS neuron'''<br /> | ||
| − | [http://{{ | + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000506.html Knoblich_mRNA_L3_CNS_neuron] <br /> |
'''L3 CNS neuroblast'''<br /> | '''L3 CNS neuroblast'''<br /> | ||
| − | [http://{{ | + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000505.html Knoblich_mRNA_L3_CNS_neuroblast] <br /> |
===Expression Levels: RNA-Seq=== | ===Expression Levels: RNA-Seq=== | ||
These tracks contain RNA-Seq expression data for several different stages of development, types of tissue culture cells, or treatment conditions. Mousing over the track in GBrowse will cause a key to pop up. The key indicates the meaning of the different colors. | These tracks contain RNA-Seq expression data for several different stages of development, types of tissue culture cells, or treatment conditions. Mousing over the track in GBrowse will cause a key to pop up. The key indicates the meaning of the different colors. | ||
| − | '''Developmental stage subsets (Baylor)''' [http://{{ | + | '''Developmental stage subsets (Baylor)''' [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000060.html BCM_1_RNAseq] Dataset report. |
| − | '''Developmental stage subsets, unique reads (modENCODE)''' [http://{{ | + | '''Developmental stage subsets, unique reads (modENCODE)''' [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000085.html modENCODE_mRNA-Seq_U] Dataset report. |
| − | '''Tissue culture cells, by strand (modENCODE Transcription Group)''' [http://{{ | + | '''Tissue culture cells, by strand (modENCODE Transcription Group)''' [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000260.htm modENCODE_mRNA-Seq_cell.B] Dataset report. |
| − | '''Treatments/Conditions''' [http://{{ | + | '''Treatments/Conditions''' [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000236.html modENCODE_mRNA-Seq_treatments] Dataset report. |
| − | ''' | + | ===Expression Levels: Small RNA-Seq=== |
| + | These tracks contain RNA-Seq expression data for small RNA species (<30nt) that have been consolidated from various independent studies by sample type (developmental stage, tissue or cell line). Different samples are presented in different colors. Configuration options allow one to choose which samples to show and which scale to use (log2 vs linear), as well as track height and layout. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Developmental stages, stranded small RNA-Seq (Lai lab)''' See [http://flybase.org/cgi-bin/fbidq.html?FBlc0000789 Lai_shortRNA-Seq'''_profiles_development] Dataset Report. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Tissues, stranded small RNA-Seq (Lai lab)''' See [http://flybase.org/cgi-bin/fbidq.html?FBlc0000790 Lai_shortRNA-Seq'''_profiles_tissues] Dataset Report. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Tissue culture cells (Schneider + embryonic), stranded small RNA-Seq (Lai lab)''' See [http://flybase.org/cgi-bin/fbidq.html?FBlc0000791 Lai_shortRNA-Seq'''_profiles_cells] Dataset Report. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Tissue culture cells (CNS, ovary, blood), stranded small RNA-Seq (Lai lab)''' See [http://flybase.org/cgi-bin/fbidq.html?FBlc0000791 Lai_shortRNA-Seq'''_profiles_cells] Dataset Report. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Tissue culture cells (imaginal disc), stranded small RNA-Seq (Lai lab)''' See [http://flybase.org/cgi-bin/fbidq.html?FBlc0000791 Lai_shortRNA-Seq'''_profiles_cells] Dataset Report. | ||
==Aberrations== | ==Aberrations== | ||
| − | '''Deleted segment'''. Indicated in red. When one or more aberrations overlap the region being viewed, a darker red bar labeled "Spanning aberration(s)" will be seen. When moused-over, a pop-up box containing all the aberrations that span the region being viewed will appear. Click one of the aberration symbols to go to the Aberration Report. When mousing over a lighter red bar labeled with a deficiency symbol, a list of genes within the aberration extents pops up. Clicking on one of the gene symbols within the pop up will link to the Gene Report. Clicking on the bar itself links to the Aberration Report. | + | '''Deleted segment'''. Indicated in red. Dashed lines indicate uncertainty in breakpoint location, and demarcate the region to which the breakpoint has been mapped. When one or more aberrations overlap the region being viewed, a darker red bar labeled "Spanning aberration(s)" will be seen. When moused-over, a pop-up box containing all the aberrations that span the region being viewed will appear. Click one of the aberration symbols to go to the Aberration Report. When mousing over a lighter red bar labeled with a deficiency symbol, a list of genes within the aberration extents pops up. Clicking on one of the gene symbols within the pop up will link to the Gene Report. Clicking on the bar itself links to the Aberration Report. |
| − | '''Duplicated segment'''. | + | '''Duplicated segment'''. Aberrations representing duplicated segments are split out into various tracks. The duplicated region is indicated in blue. When one or more aberrations cover the region being viewed, a darker blue bar labeled "Spanning aberration(s)" will be seen. When moused-over, a pop-up box containing all the aberrations that cover the region being viewed will appear. Click one of the aberration symbols to go to the Aberration Report. When mousing over a lighter blue bar labeled with a duplication symbol, a list of genes within the aberration extents pops up. Clicking on one of the gene symbols within the pop up will link to the Gene Report. Clicking on the bar itself links to the Aberration Report. |
| + | *'''Y linked duplication''' Interchromosomal duplications inserted onto the Y chromosome. | ||
| + | *'''Transgenic duplication''' Interchromosomal duplications generated by transgenic methods, excluding those carried on the Y chromosome. Duplicated region is indicated in blue. | ||
| + | *'''Other duplicated segment''' Duplicated segments not part of the Y-linked or transgenic duplication series. Duplicated region is indicated in blue. | ||
| − | '''Stock | + | '''Stock Center Aberration: deleted segment'''. This track functions just as the "Deleted Segment" track described above. This track contains only deficiencies available from the Bloomington Stock Center. Links to the relevant Stock Report can be found at the bottom of the Aberration Report, which is linked from the feature glyph. |
| − | '''Stock | + | '''Stock Center Aberration: duplicated segment''' This track functions just as the "Duplicated Segment" track described above. This track contains only duplications available from the Bloomington Stock Center. Links to the relevant Stock Report can be found at the bottom of the Aberration Report, which is linked from the feature glyph. |
'''The Bloomington Deficiency Kit''': | '''The Bloomington Deficiency Kit''': | ||
| Line 261: | Line 340: | ||
'''BDSC Deficiency Kit: deleted segment''' Molecularly defined deficiencies are indicated in red. Click the deficiency to go to the Aberration Report. Links to the relevant Stock Report can be found at the bottom of the Aberration Report. <br /> | '''BDSC Deficiency Kit: deleted segment''' Molecularly defined deficiencies are indicated in red. Click the deficiency to go to the Aberration Report. Links to the relevant Stock Report can be found at the bottom of the Aberration Report. <br /> | ||
| − | [http://{{ | + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000501.html Dfs_BSC_set2] Dataset report. <br /> |
| − | [http://{{ | + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000496.html Dfs_BSC_set1] Dataset report. <br /> |
'''BDSC Deficiency Kit: gap filling or haploinsufficiency flanking segment.''' Segments of cytologically defined deficiencies that fill gaps between molecularly defined deficiencies or flank haploinsufficient loci are indicated in yellow. Click the segment icon to go to the Aberration Report for the full deficiency. Links to the relevant Stock Report can be found at the bottom of the Aberration Report. | '''BDSC Deficiency Kit: gap filling or haploinsufficiency flanking segment.''' Segments of cytologically defined deficiencies that fill gaps between molecularly defined deficiencies or flank haploinsufficient loci are indicated in yellow. Click the segment icon to go to the Aberration Report for the full deficiency. Links to the relevant Stock Report can be found at the bottom of the Aberration Report. | ||
| Line 270: | Line 349: | ||
'''DRSC RNAi amplicons''' <br /> | '''DRSC RNAi amplicons''' <br /> | ||
Extents of the amplicons are indicated with an orange bar. <br /> | Extents of the amplicons are indicated with an orange bar. <br /> | ||
| − | [http://{{ | + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000026.html DRSC dsNRA amplicon platform] Dataset Report. DNA fragments amplified from D. melanogaster genomic DNA (OregonR) by the Drosophila Genomics Resource Center (DGRC), using gene-specific primers made by Incyte and designed to target transcribed regions with minimal sequence similarity to other genes. Used for the DGRC-D.melanogaster-DGRC1-15552-v5 amplicon microarray, release date June 2, 2006 (original release of v1, May 2004) . For further information see the [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000027.html DGRC-1 Dataset report]. |
'''VDRC RNAi amplicons''' <br /> | '''VDRC RNAi amplicons''' <br /> | ||
Extents of the amplicons are indicated with an orange bar. <br /> | Extents of the amplicons are indicated with an orange bar. <br /> | ||
| − | Segment used to create inverted repeat in RNAi construct from the Vienna Drosophila RNAi Center ([http://{{ | + | Segment used to create inverted repeat in RNAi construct from the Vienna Drosophila RNAi Center ([http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBrf0200327.html Dickson B. et al. 2007.7.18]). "GD" identifer also used for allele and construct symbols. <br /> |
| − | [http://{{ | + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000041.html VDRC-1] Dataset Report<br /> |
| − | [http://{{ | + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000055.html VDRC-2] Dataset Report. <br /> |
'''TRiP RNAi amplicons''' <br /> | '''TRiP RNAi amplicons''' <br /> | ||
Extents of the amplicons are indicated with an orange bar. <br /> | Extents of the amplicons are indicated with an orange bar. <br /> | ||
| − | FBlc0000048 [http://{{ | + | FBlc0000048 [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000048.html TRiP-1] Dataset Report <br /> |
| − | FBlc0000153 [http://{{ | + | FBlc0000153 [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000153.html TRiP-2] Dataset Report<br /> |
| − | FBlc0000185 [http://{{ | + | FBlc0000185 [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000185.html TRiP-3] Dataset Report<br /> |
| − | FBlc0000186 [http://{{ | + | FBlc0000186 [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000186.html TRiP-4] Dataset Report<br /> |
| − | FBlc0000416 [http://{{ | + | FBlc0000416 [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000416.html TRiP-5] Dataset Report<br /> |
'''BKNA RNAi amplicons''' <br /> | '''BKNA RNAi amplicons''' <br /> | ||
Extents of the amplicons are indicated with an orange bar. <br /> | Extents of the amplicons are indicated with an orange bar. <br /> | ||
| − | [http://{{ | + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000030.html HD2] Dataset Report (dsRNA amplicon platform) RNAi amplicons from the GenomeRNAi database. <br /> |
'''HFA RNAi amplicons''' <br /> | '''HFA RNAi amplicons''' <br /> | ||
Extents of the amplicons are indicated with an orange bar. <br /> | Extents of the amplicons are indicated with an orange bar. <br /> | ||
| − | [http://{{ | + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000031.html HFA] Datset Report. |
'''NIG-Fly RNAi amplicons''' <br /> | '''NIG-Fly RNAi amplicons''' <br /> | ||
Extents of the amplicons are indicated with an orange bar. <br /> | Extents of the amplicons are indicated with an orange bar. <br /> | ||
| − | [http://{{ | + | [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000491.html NIG_RNAi_Fly-1] Datset Report. |
| + | |||
| + | == sgRNA Reagents == | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''TRiP-OE sgRNAs (overexpression)''' <br/> | ||
| + | Genomic sequences used as short guide RNAs in UAS constructs designed to target genes for CRISPR/Cas9-VPR-based overexpression. Extents of sgRNAs are indicated by red glyphs (arrows indicate orientation). Two nearby sgRNAs are used in a single construct to target the upstream region of a given gene.<br /> | ||
| + | Example region: 2L:7305255..7308450<br /> | ||
| + | More information: [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0003381.html TRiP-OE] report | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''TRiP-KO sgRNAs (knockout)''' <br/> | ||
| + | Genomic sequences used as short guide RNAs in UAS constructs designed to target genes for CRISPR/Cas9-based mutation. Extents of sgRNAs are indicated by red glyphs (arrows indicate orientation).<br /> | ||
| + | Example region: 2R:16654718..16655037<br /> | ||
| + | More information: [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0003382.html TRiP-KO] report | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Predicted sgRNAs''' <br/> | ||
| + | Sequences predicted to be suitable as sgRNAs for genome engineering. These comprise all possible 23-mers in the D. melanogaster Release6 genome assembly that have 1) a 3-prime PAM sequence (NGG) and 2) a 15 bp sequence that is unique to the genome (including the PAM sequence). The seed score for each sgRNA, which ranges from 12 to 15 bases, indicates the uniqueness of the base pairing end of the sgRNA (excluding the PAM sequence). The frameshift score is the percent of frameshift changes predicted by micro-homology around the target site; the higher the score, the better suited the sgRNA for knockout. Because base pair mismatches can be tolerated outside the seed region, predicted sgRNAs were evaluated for potential off-target sites allowing for 3, 4 or 5 mismatches; potential sgRNA sequences are sorted into five browser tracks based on their predicted specificity at different stringencies.<br /> | ||
| + | Example region: 2L:7314441..7314673<br /> | ||
| + | More information: [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0003481.html DRSC_sgRNA_designs] report | ||
==Other Reagents== | ==Other Reagents== | ||
| − | '''Putative brain enhancers''' (Pfeiffer et al.) [http://{{ | + | '''Putative brain enhancers''' [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBrf0205679.html (Pfeiffer et al.)] [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000201.html GMR_Brain_exp_1] Dataset Report. Glyphs represent putative enhancers used to generate fly stocks carrying GAL4 transgenic constructs designed to be expressed in adult brain. Stocks are available from the Bloomington Stock Center. Clicking the glyph brings up the associated Sequence Feature report (e.g. http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBsf0000162377.html). On the Sequence Feature report, under "associated information" there is a construct listed. Clicking this construct link brings up the associated Construct Report (e.g. http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBtp0058072.html) on which you can find a link to the Stock Report (e.g. http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBst0045107.html). Sorry it's so roundabout! |
| + | |||
| + | '''VDRC Vienna Tiles GAL4 lines''' [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000718.html VDRC-VT] Dataset Report. Glyphs represent putative enhancers used to generate fly stocks carrying GAL4 transgenic constructs. Stocks are available from the Vienna Drosophila Resource Center. Clicking the glyph brings up the associated Sequence Feature report (e.g. [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBsf0000446638.html VT020839]), with links to the related stock reports. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Tiling BACs''' Tiling BAC indicated by narrow gray bar. BAC genomic clones used by the Berkeley Drosophila Genome Project as part of the minimal tiling path used for determination of the D. melanogaster genomic sequence ([http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBrf0155823.html Celniker SE. et al. 2002]). | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Pacman Chori-321_BAC''' [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000783.html CHORI-321_BAC] Dataset Report. The blue glyphs indicate the extent of the BAC, inferred from the mapping of the sequenced BAC insert ends; CHORI-321 BAC inserts are, on average, 83 kbp in size. | ||
| − | ''' | + | '''Pacman Chori-322_BAC''' [http://{{flybaseorg}}/reports/FBlc0000784.html CHORI-322_BAC] Dataset Report. The blue glyphs indicate the extent of the BAC, inferred from the mapping of the sequenced BAC insert ends; CHORI-322 BAC inserts are, on average, 21 kbp in size. |
| − | == | + | == BLAST Hit == |
| − | ''' | + | '''BLAST HSP''' If entry into GBrowse was via a linked hit using the FlyBase BLAST tool, the extent of the aligned region is shown as a vertical grey bar that extends through all the GBrowse tiers. |
==Analysis== | ==Analysis== | ||
'''Restriction Sites''' Clicking here marks cut sites for the common restriction enzymes PvuII, ClaI, BamHI, EcoRI. | '''Restriction Sites''' Clicking here marks cut sites for the common restriction enzymes PvuII, ClaI, BamHI, EcoRI. | ||
Latest revision as of 17:45, 14 December 2022
| Warning |
|---|
| Information about GBrowse is only relevant to users of an archived instance of FlyBase earlier than FB2022_05.
For users working with the current release at flybase.org, please see our page about FlyBase:JBrowse, the genome viewer that replaced GBrowse. |
Updated 21 December 2017
Below is a detailed list of tracks available on the D. melanogaster GBrowse viewer.
Reference Genome Annotations (iso-1)
Note: The genome release is shown in the top right corner of the screen, e.g. D. melanogaster (R6.07). The number before the decimal refers to the version of the genome sequence, currently, Release 6 (R6) (Hoskins et al, 2015), which does not change between major releases. The number after the decimal point refers to the version of the annotation set, which may be updated at each release. The D. melanogaster gene set consists of gene models manually annotated by FlyBase annotators (with the exception of some classes of small non-coding RNAs) (Matthews, et al., (2015). G3 (Bethesda) 5(5):777-801).
Gene Span Shows the total extent of the transcribed region of an annotated gene (including non-coding genes), with direction of transcription indicated. No transcript substructure is shown; corresponds to the entire extent defined by all annotated transcripts. Hyperlinked to Gene Report; label shows FlyBase gene symbol.
Transcript SO:0000673 Shows the exon (wider bars) and intron (black line) structure of each annotated coding transcript, with direction of transcription indicated. Hyperlinked Transcript Report; if label option is on, shows FlyBase symbol.
CDS Shows extent of sequence encoding each specific polypeptide, with direction of transcription indicated; introns indicated as narrow lines. Hyperlinked to Polypeptide Report; if label option is on, shows FlyBase symbol.
Natural TE SO:0000101 Shows the extent of a natural transposable element in the sequenced strain (at the time it was sequenced). Hyperlinked to Natural Transposon report; if label option is on, shows FlyBase symbol.
Repeat region Regions of genomic repeats and low complexity DNA sequences, as computed using RepeatMasker and RepeatRunner (Smith, et al., 2007).
General
Estimated Cytological band Approximate extent of the classical cytological chromosome bands described by Bridges. See Computed cytological data in FlyBase for a detailed description of how this computed cytological location is calculated. See FlyBase Maps for a collection of polytene chromosome images.
3-frame translation (forward) If zoomed out (greater than 400bp), shows ticks at sites of stop codons for the three frames on the forward strand. If zoomed in (400bp or less), shows predicted translations for each frame, using single-letter amino acid code.
3-frame translation (reverse) If zoomed out (greater than 400bp), shows ticks at sites of stop codons for the three frames on the reverse strand. If zoomed in (400bp or less), shows predicted translations for each frame, using single-letter amino acid code.
DNA/GC Content If zoomed out (greater than 100bp) shows a graphic of GC content calculated over 10bp intervals. If zoomed in (100bp or less), shows the double-stranded DNA sequence.
Aligned Evidence
cDNA D. melanogaster cDNA sequences from large-scale submissions submitted to the sequence databases; shows the exon (wider bars) and intron (black line) structure, and direction of transcription. Sequences are aligned to release 6 by NCBI and submitted to FlyBase. Some genomic DNA submissions, including third party submissions, are included in this tier.
EST ("expressed sequence tag") Indicated in light green. Partial sequence of a cDNA; shows the exon (wider bars) and intron (narrow bars) structure, and direction of transcription. Sequences are aligned to release 6 by NCBI and submitted to FlyBase.
other aligned sequences D. melanogaster aligned nucleotides submitted to the sequence databases. Sequences are aligned to release 6 by NCBI and submitted to FlyBase. Some genomic DNA submissions, including third party submissions, are included in this tier.
RNA-Seq based exon junctions Indicated in blue. Orientation of the junction is indicated by an arrowhead in the center of the junction. Mousing over the glyph for a RNA-Seq junction activates a pop-up indicating the total read counts for the junction. The read counts are separated based upon which dataset the information is from (modENCODE or Baylor, see below for Dataset Report links). See the BCM_1_RNAseq_junctions and modENCODE_mRNA-Seq_U_junctions Dataset Reports.
PeptideAtlas peptides Indicated in yellow. Alignment of peptide sequences determined by mass spectroscopy, derived from polypeptides isolated from the sequenced strain at various developmental stages. Contributed by the Center for Model Organism Proteomes, SystemsX and Research Priority Project of the University of Zurich, Switzerland. For more information, see Peptide Atlas
Transcription Start Sites (modENCODE), embryo Transcription start site (TSS) regions identified by integrative analysis of ESTs, CAGE or RLM-RACE, modENCODE. The horizontal extent of the blue arrow indicates the range over which 90 percent of the TSS signal is located. The red bars indicate TSS usage at single base resolution along the genome. Clicking on the TSS feature will link to the relevant Sequence Feature report. Note: data for embryonic stages only. See the mE_Transcription_Start_Sites Dataset Report.
Transcription Start Sites (RAMPAGE), peak calls Transcription start site regions (peak calls) identified by RAMPAGE-Seq across 36 stages of development, depicted as green arrow glyphs. The arrow points in the direction of transcription.
Transcription Start Sites (RAMPAGE), early embryo 0-12hr, stranded RNA-Seq Profile of capped transcript 5' ends observed by RAMPAGE-Seq for 12 stages of early embryogenesis.
Transcription Start Sites (RAMPAGE), late embryo 13-24hr, stranded RNA-Seq Profile of capped transcript 5' ends observed by RAMPAGE-Seq for 12 stages of late embryogenesis.
Transcription Start Sites (RAMPAGE), larva/pupa/adult, stranded RNA-Seq Profile of capped transcript 5' ends observed by RAMPAGE-Seq for 12 larval, pupal or adult stages.
See the TSS_RAMPAGE Dataset Report.
Transcription Start Sites (MachiBase), stranded RNA-Seq Profile of capped transcript 5' ends observed by MachiBase CAGE-Seq for embryonic, larval, adult male and female (young or old) and S2 cell line samples. See the TSS_MachiBase Dataset Report.
Please note that the signal shown for the Transcription Start Site data (RAMPAGE and MachiBase) is one base off: i.e., the signal is shown one base to the left of where it should be. In the example to the right, the signal should map to the first base (3R:6864324, A) of the ftz transcript, but is instead shown one base to the left (3R:6864323, C). This is a known bug and we're working to fix this.
Protein domains (PFAM) Pfam protein domains identified in annotated proteins, as obtained from InterPro, are mapped to the genome.
Protein domains (SMART) SMART protein domains identified in annotated proteins are mapped to the genome.
RNA Editing Sites A-to-I RNA editing sites.
mE_A-to-I_RNA_Editing_Sites Dataset Report.
Rosbash_Adult_Head_A-to-I_Editing_Sites Dataset Report.
Mapped Mutations
Transgene insertion site SO:0000368 Thin rectangles indicate the site of transposon insertion. If the estimated insertion range is larger than 10 nucleotides, there are short dashes on either side of the rectangle. In those cases, see the Insertion Report for more information about localization. If known, the orientation of the transposon (relative to that transposon's inherent asymmetry) is indicated by an arrow (pointing 5'-to-3'). To determine the orientation of functional elements within a transposon (e.g., FRT, UAS, etc.), consult the FlyBase construct reports, as described in this guide.
Transgenic insertions in stocks, Bloomington SO:0000368 This track functions just as the "Transgenic Insertion Site" track described above. This track contains only insertions available from the Bloomington Stock Center. Links to the relevant Stock Report can be found at the bottom of the Insertion Report, which is linked from the feature glyph.
Transgenic insertions in stocks, Kyoto SO:0000368 This track functions just as the "Transgenic Insertion Site" track described above. This track contains only insertions available from the Kyoto Stock Center. Links to the relevant Stock Report can be found at the bottom of the Insertion Report, which is linked from the feature glyph.
Transgenic insertions in stocks, Harvard SO:0000368 This track functions just as the "Transgenic Insertion Site" track described above. This track contains only insertions available from the Harvard Medical School Stock Center. Links to the relevant Stock Report can be found at the bottom of the Insertion Report, which is linked from the feature glyph.
Point mutation SO:1000008 A single nucleotide has been changed into another nucleotide. Location of mutation is indicated with a grey bar and labeled with the FlyBase allele symbol. The feature glyph is linked to the related Allele Report.
Sequence variant SO:0000109 A region of sequence where variation has been observed. Often these refer to natural variants of a protein that lead to two different functions. The location of the mutation is indicated with a grey bar and labeled with the FlyBase allele symbol. The feature glyph is linked to the related Allele Report.
Uncharacterized change in nucleotide sequence SO:1000007 The nature of the nucleotide substitution is either uncharacterized or only partially characterized. The location of the mutation is indicated with grey bar and labeled with the FlyBase allele symbol. The feature glyph is linked to the related Allele Report.
Aberration junction SO:0000687 Location of aberration breakpoint reported in the literature. Labeled with FlyBase aberration symbol designation and the numerical designation of the breakpoint mapped (where known). Often the exact breakpoint location is unknown and the feature indicates a range within which the breakpoint has been mapped. Genetic data is available in the Aberration Report which can be accessed directly by clicking on the feature.
Complex substitution SO:1000005 The mutation does not fall simply into any of the other categories and is often a combination of events, e.g. deletion of 20 bases and insertion of 11 unrelated bases. Location of mutation is indicated with a grey bar and labeled with the FlyBase allele symbol. Feature is linked to the related Allele Report.
Indel SO:1000032 The junction where an insertion or deletion of one or more nucleotides occurred. Location of mutation is indicated with a grey bar and labeled with the FlyBase allele symbol. In the case of deletions, the extent of the deletion is indicated by a grey bar. In the case of nucleotide insertions, the location of the nucleotide(s) insertion is indicated by a vertical grey line. Features are linked to the related Allele Report.
Rescue fragment SO:0000411 Locations of transgenic rescue fragment reported in the literature. Labeled with FlyBase allele symbol designation. Features are linked to the related Allele Reports which contain genetic data.
Gene Predictions
NCBI gnomon, 2006 (coding region of transcript) generated via a hidden Markov model using transcript alignment constraints and protein hit information, if available; allows prediction of alternatively spliced isoforms (Souvorov, et al., 2006, NCBI); submitted by J. Ostell.
CONTRAST (coding region of transcript) using a semi-Markov conditional random field (Gross, Do, and Batzoglou, 2005, BCATS 2005 Symposium Proceedings, p. 82); submitted by S. Batzoglou.
PhyloCSF (CONGO) Exon prediction. Region of sequence conservation across multiple Drosophila species, with a pattern of conservation indicative of a protein-coding extent and termini consistent with exon structure (start, splice or stop); submitted by M. Lin and M. Kellis. Related publications: Lin MF, Carlson, JW et al. (2007), Lin MF, Jungreis I, and Kellis M. (2011)
Similarity
Proteins (aligned by BLAST)
Dmel proteins D. melanogaster protein sequences submitted to the sequence databases. Proteins are aligned to release 6 by NCBI and submitted to FlyBase.
Other proteins Protein sequences submitted to the sequence databases since 2003, from species other than D. melanogaster; Proteins are aligned to release 6 by NCBI and submitted to FlyBase.
Synteny Features
Orthologs. Indicated by yellow bar covering extent of the orthologous region. Mousing over this bar will cause a pop-up box to appear which will contain links for all of the orthologs of the gene. The ortholog box will contain the drosophilid orthologs on the left and other orthologs on the right.
Noncoding Features
Insulators (modENCODE, class I) Insulator_Class_I.mE01 Dataset Report
Insulators (modENCODE, class II) Insulator_Class_II.mE01 Dataset Report
TFBS (EMSA, footprinting). Indicated by grey bar. Locations of protein binding sites reported in the literature, as compiled by FlyBase and/or REDfly). Reference and supporting information available on related Sequence Feature reports (click feature glyph to access report). See also the REDfly TFBSs dataset report.
Putative PREs (modENCODE) mE1_HDAC_PRE Dataset Report. Genomic sequences identified as putative polycomb response elements (silencers) in embryos.
Transcriptional Regulatory Regions (REDfly). Indicated by grey bar. Locations of regulatory regions reported in the literature, as compiled by FlyBase and/or REDfly). Reference and supporting information available on related Sequence Feature reports (click feature glyph to access report). See also the REDfly CRMs dataset report.
ChIP (whole embryo) – TF HOT spot analysis mE1_TFBS_HSA Dataset Report. Genomic sequences identified as unique regions of transcription factor (TF) binding using HOT spot analysis (HSA); one or many TFs may bind in a given region. A synthesis of ChIP data sets for 41 different transcription factors. TF binding profiles used in this analysis were assayed at early embryo stages. Mousing over the feature pops up a box that lists the transcription factor genes that bind within the region. Clicking on the feature links to the related Sequence Feature report.
ChIP (whole embryo) – zinc finger TFs Binding sites for transcriptions factors that contain one or more zinc finger domains. Clicking on the feature links to the related Sequence Feature report. The following Dataset Reports comprise the data found in this track.
mE1_TFBS_disco
mE1_TFBS_ftz-f1
mE1_TFBS_GATAe
BDTNP1_TFBS_hb
mE1_TFBS_hkb
BDTNP1_TFBS_kni
mE1_TFBS_Kr
mE1_TFBS_sbb
mE1_TFBS_sens
BDTNP1_TFBS_shn
BDTNP1_TFBS_sna
BDTNP1_TFBS_tll
mE1_TFBS_zfh1
ChIP (whole embryo) – homeodomain TFs Binding sites for transcriptions factors that contain one or more homeodomains. The following Dataset Reports comprise the data found in this track.
BDTNP1_TFBS_bcd
mE1_TFBS_cad
mE1_TFBS_Dll
mE1_TFBS_en
mE1_TFBS_eve
BDTNP1_TFBS_ftz
mE1_TFBS_inv
BDTNP1_TFBS_prd
mE1_TFBS_Ubx
BDTNP1_TFBS_z
ChIP (whole embryo) – helix-loop-helix TFs Binding sites for transcriptions factors that contain one or more helix-loop-helix domains. The following Dataset Reports comprise the data found in this track.
BDTNP1_TFBS_da
mE1_TFBS_h
mE1_TFBS_kn
BDTNP1_TFBS_twi
ChIP (whole embryo) – BTB/POZ TFs Binding sites for transcriptions factors that contain one or more BTB/POZ domains. The following Dataset Reports comprise the data found in this track.
mE1_TFBS_bab1
mE1_TFBS_chinmo
mE1_TFBS_Trl
mE1_TFBS_ttk
ChIP (whole embryo) – other TFs Binding sites for transcriptions factors that do not fall into one of the other categories. The following Dataset Reports comprise the data found in this track.
mE1_TFBS_cnc
mE1_TFBS_D
BDTNP1_TFBS_dl
BDTNP1_TFBS_gt
mE1_TFBS_jumu
BDTNP1_TFBS_Mad
BDTNP1_TFBS_Med
mE1_TFBS_run
BDTNP1_TFBS_slp1
mE1_TFBS_Stat92E
ChIP (mesoderm) - various TFs ChIP-chip binding peak calls for 13 TFs that control mesodermal development at various points of embryogenesis. There are 28 samples in all, displayed as distinct subtracks (use the subtrack selection menu to turn subtracks on/off and reorder them). These data were kindly provided by Eileen Furlong's lab (EMBL), comprising several studies: Zinzen et al., 2009, Bonn et al., 2012, Junion et al., 2012, Rembold et al., 2014 and Ciglar et al., 2014. These 28 ChIP-chip datasets were processed in parallel by Matthias Monfort of the Furlong group, as described here. More details on each subtrack are available in the FlyBase dataset reports, with links to the appropriate data repository.
ChIP-chip_bap_E6-8h_organism
ChIP-chip_bin_E6-8h_organism
ChIP-chip_bin_E8-10h_organism
ChIP-chip_bin_E10-12h_organism
ChIP-chip_Doc2_E4-6h_organism
ChIP-chip_Doc2_E6-8h_organism
ChIP-chip_lmd_E6-8h_organism
ChIP-chip_pMad_E4-6h_organism
ChIP-chip_pMad_E6-8h_organism
ChIP-chip_Mef2_E2-4h_organism
ChIP-chip_Mef2_E4-6h_organism
ChIP-chip_Mef2_E6-8h_organism
ChIP-chip_Mef2_E8-10h_organism
ChIP-chip_Mef2_E10-12h_organism
ChIP-chip_pan_E4-6h_organism
ChIP-chip_pan_E6-8h_organism
ChIP-chip_pnr_E4-6h_organism
ChIP-chip_pnr_E6-8h_organism
ChIP-chip_slp1_E4-6h_organism
ChIP-chip_slp1_E6-8h_organism
ChIP-chip_sna_E2-4h_organism
ChIP-chip_tin_E2-4h_organism
ChIP-chip_tin_E4-6h_organism
ChIP-chip_tin_E6-8h_organism
ChIP-chip_ttk_E6-8h_organism
ChIP-chip_twi_E2-4h_organism
ChIP-chip_twi_E4-6h_organism
ChIP-chip_twi_E6-8h_organism
ChIP (mesoderm) - His3 modifications Peak calls for ChIP-seq of histone modifications obtained from purified embryonic mesodermal nuclei. Data are available for H3K4me1, H3K4me3, H3K27Ac, H3K27me3, H3K36me3, H3K79me3 and RNA Pol II, displayed as 7 distinct subtracks. Data were kindly provided by Eileen Furlong's lab (EMBL), as published in Bonn et al., 2012. Data analysis methods by Matthias Monfort (of the Furlong group) are described here. More details on each subtrack are available in the FlyBase dataset reports, with links to the appropriate data repository.
ChIP-seq_H3K4me1_E6-8h_mesoderm
ChIP-seq_H3K27Ac_E6-8h_mesoderm
ChIP-seq_H3K4me3_E6-8h_mesoderm
ChIP-seq_RpII33_E6-8h_mesoderm
ChIP-seq_H3K79me3_E6-8h_mesoderm
ChIP-seq_H3K36me3_E6-8h_mesoderm
ChIP-seq_H3K27me3_E6-8h_mesoderm
Chromatin domains 5-state model, Kc cells Chromatin_types_NKI.Kc167 Dataset Report. Whole-genome DamID binding profiles of 53 chromatin proteins in Drosophila Kc167 cells were generated and/or analyzed. In the same array platform, ChIP-on-chip profiles of histone H3, H1, H3K9me2, H3K27me3, H3K4me2, and H3K79me3 were obtained. These were correlated with gene expression, which was measured by RNA-tag profiling.
Chromatin domains 9-state model, S2 cells Chromatin_types_mE1.S2 Dataset Report. Demarcation of chromatin domains of nine major types based on analysis of 18 histone modification profiles.
Chromatin domains 9-state model, BG3 cells Chromatin_types_mE2.BG3 Dataset Report. Demarcation of chromatin domains of nine major types based on analysis of 18 histone modification profiles.
Origins of replication mE_Early_Replication_Origins_cells and mE_Orc2_ChIP-Seq_cells Dataset Reports. Genome profile of early activating origins of replication, based on BrdU label or Orc2 binding, characterized in Kc167, ML-DmBG3-c2 and S2-DRSC cell lines.
Microarray Features
Affymetric v1 Affymetrix_GeneChip_v1 Dataset Report. Oligonucleotides (25-mers) designed by Affymetrix to correspond to annotated transcripts in D. melanogaster. Used for the Affymetrix GeneChip Drosophila Genome Array DrosGenome1 microarray, release date February 19, 2002.
Affymetric v2 Affymetrix_GeneChip_v2 Dataset Report. Oligonucleotides (25-mers) designed by Affymetrix to correspond to annotated transcripts in D. melanogaster. Used for the Affymetrix GeneChip Drosophila Genome 2.0 Array, release date July 1, 2004.
DGRC-1 amplicons DGRC-1 Dataset Report. Indicated in orange. DNA fragments amplified from D. melanogaster genomic DNA (OregonR) by the Drosophila Genomics Resource Center (DGRC), using gene-specific primers made by Incyte and designed to target transcribed regions with minimal sequence similarity to other genes. Used for the DGRC-D.melanogaster-DGRC1-15552-v5 amplicon microarray, release date June 2, 2006 (original release of v1, May 2004) . For further information see the DGRC-1 library collection report.
DGRC-2 oligos DGRC-2 Dataset Report. Indicated in orange. "Long oligos" (65-69mers) designed to correspond to annotated transcripts in D. melanogaster (r4.3); synthesized by FlyChip in collaboration with the International Drosophila Array Consortium INDAC and the Drosophila Genomics Resource Center (DGRC). Used for the DGRC-D.melanogaster-DGRC2-17328-v1 oligonucleotide microarray, release date June 20,2006. For further information see the DGRC-2 library collection report.
Expression Levels
Expression Levels: RNA-Seq by Tissue
To aid in visualization, we have divided the RNA-Seq by Tissue data into five categories listed below. The datasets included within each category are also listed. Mousing over the Topoview glyph in GBrowse will cause a color-key to pop up so you can tell which dataset you are looking at.
Digestive system
mE_mRNA_L3_Wand_dig_sys
mE_mRNA_A_1d_dig_sys
mE_mRNA_A_4d_dig_sys
mE_mRNA_A_20d_dig_sys
Fat body and salivary glands
mE_mRNA_L3_Wand_fat
mE_mRNA_WPP_fat
mE_mRNA_P8_fat
mE_mRNA_L3_Wand_saliv
mE_mRNA_WPP_saliv
Imaginal disc and other carcass
mE_mRNA_L3_Wand_imag_disc
mE_mRNA_L3_Wand_carcass
mE_mRNA_A_1d_carcass
mE_mRNA_A_4d_carcass
mE_mRNA_A_20d_carcass
CNS and adult head
mE_mRNA_L3_CNS
mE_mRNA_P8_CNS
mE_mRNA_A_MateM_1d_head
mE_mRNA_A_MateM_4d_head
mE_mRNA_A_MateM_20d_head
mE_mRNA_A_VirF_1d_head
mE_mRNA_A_VirF_4d_head
mE_mRNA_A_VirF_20d_head
mE_mRNA_A_MateF_1d_head
mE_mRNA_A_MateF_4d_head
mE_mRNA_A_MateF_20d_head
Gonads and male accessory glands
mE_mRNA_A_MateM_4d_testis
mE_mRNA_A_MateM_4d_acc_gland
mE_mRNA_A_VirF_4d_ovary
mE_mRNA_A_MateF_4d_ovary
L3 CNS neuron
Knoblich_mRNA_L3_CNS_neuron
L3 CNS neuroblast
Knoblich_mRNA_L3_CNS_neuroblast
Expression Levels: RNA-Seq
These tracks contain RNA-Seq expression data for several different stages of development, types of tissue culture cells, or treatment conditions. Mousing over the track in GBrowse will cause a key to pop up. The key indicates the meaning of the different colors.
Developmental stage subsets (Baylor) BCM_1_RNAseq Dataset report.
Developmental stage subsets, unique reads (modENCODE) modENCODE_mRNA-Seq_U Dataset report.
Tissue culture cells, by strand (modENCODE Transcription Group) modENCODE_mRNA-Seq_cell.B Dataset report.
Treatments/Conditions modENCODE_mRNA-Seq_treatments Dataset report.
Expression Levels: Small RNA-Seq
These tracks contain RNA-Seq expression data for small RNA species (<30nt) that have been consolidated from various independent studies by sample type (developmental stage, tissue or cell line). Different samples are presented in different colors. Configuration options allow one to choose which samples to show and which scale to use (log2 vs linear), as well as track height and layout.
Developmental stages, stranded small RNA-Seq (Lai lab) See Lai_shortRNA-Seq_profiles_development Dataset Report.
Tissues, stranded small RNA-Seq (Lai lab) See Lai_shortRNA-Seq_profiles_tissues Dataset Report.
Tissue culture cells (Schneider + embryonic), stranded small RNA-Seq (Lai lab) See Lai_shortRNA-Seq_profiles_cells Dataset Report.
Tissue culture cells (CNS, ovary, blood), stranded small RNA-Seq (Lai lab) See Lai_shortRNA-Seq_profiles_cells Dataset Report.
Tissue culture cells (imaginal disc), stranded small RNA-Seq (Lai lab) See Lai_shortRNA-Seq_profiles_cells Dataset Report.
Aberrations
Deleted segment. Indicated in red. Dashed lines indicate uncertainty in breakpoint location, and demarcate the region to which the breakpoint has been mapped. When one or more aberrations overlap the region being viewed, a darker red bar labeled "Spanning aberration(s)" will be seen. When moused-over, a pop-up box containing all the aberrations that span the region being viewed will appear. Click one of the aberration symbols to go to the Aberration Report. When mousing over a lighter red bar labeled with a deficiency symbol, a list of genes within the aberration extents pops up. Clicking on one of the gene symbols within the pop up will link to the Gene Report. Clicking on the bar itself links to the Aberration Report.
Duplicated segment. Aberrations representing duplicated segments are split out into various tracks. The duplicated region is indicated in blue. When one or more aberrations cover the region being viewed, a darker blue bar labeled "Spanning aberration(s)" will be seen. When moused-over, a pop-up box containing all the aberrations that cover the region being viewed will appear. Click one of the aberration symbols to go to the Aberration Report. When mousing over a lighter blue bar labeled with a duplication symbol, a list of genes within the aberration extents pops up. Clicking on one of the gene symbols within the pop up will link to the Gene Report. Clicking on the bar itself links to the Aberration Report.
- Y linked duplication Interchromosomal duplications inserted onto the Y chromosome.
- Transgenic duplication Interchromosomal duplications generated by transgenic methods, excluding those carried on the Y chromosome. Duplicated region is indicated in blue.
- Other duplicated segment Duplicated segments not part of the Y-linked or transgenic duplication series. Duplicated region is indicated in blue.
Stock Center Aberration: deleted segment. This track functions just as the "Deleted Segment" track described above. This track contains only deficiencies available from the Bloomington Stock Center. Links to the relevant Stock Report can be found at the bottom of the Aberration Report, which is linked from the feature glyph.
Stock Center Aberration: duplicated segment This track functions just as the "Duplicated Segment" track described above. This track contains only duplications available from the Bloomington Stock Center. Links to the relevant Stock Report can be found at the bottom of the Aberration Report, which is linked from the feature glyph.
The Bloomington Deficiency Kit:
The Bloomington Deficiency Kit is a set of stocks defined by the Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center (BDSC) to provide maximal coverage of the genome with the minimal number of deficiencies having molecularly mapped breakpoints. The BDSC Deficiency Kit also includes deficiencies with breakpoints that have not been mapped molecularly, primarily to provide coverage of gaps between the molecularly defined deficiencies. Since the ends of cytologically characterized deficiencies cannot be placed on the genome map with certainty, the BDSC has defined segments of these deficiencies that fill gaps in molecularly defined coverage for GBrowse display. The endpoints of gap filling segments are derived primarily from overlapping deficiency endpoints and complementation with annotated genes.
BDSC Deficiency Kit: deleted segment Molecularly defined deficiencies are indicated in red. Click the deficiency to go to the Aberration Report. Links to the relevant Stock Report can be found at the bottom of the Aberration Report.
Dfs_BSC_set2 Dataset report.
Dfs_BSC_set1 Dataset report.
BDSC Deficiency Kit: gap filling or haploinsufficiency flanking segment. Segments of cytologically defined deficiencies that fill gaps between molecularly defined deficiencies or flank haploinsufficient loci are indicated in yellow. Click the segment icon to go to the Aberration Report for the full deficiency. Links to the relevant Stock Report can be found at the bottom of the Aberration Report.
RNAi Reagents and Data
DRSC RNAi amplicons
Extents of the amplicons are indicated with an orange bar.
DRSC dsNRA amplicon platform Dataset Report. DNA fragments amplified from D. melanogaster genomic DNA (OregonR) by the Drosophila Genomics Resource Center (DGRC), using gene-specific primers made by Incyte and designed to target transcribed regions with minimal sequence similarity to other genes. Used for the DGRC-D.melanogaster-DGRC1-15552-v5 amplicon microarray, release date June 2, 2006 (original release of v1, May 2004) . For further information see the DGRC-1 Dataset report.
VDRC RNAi amplicons
Extents of the amplicons are indicated with an orange bar.
Segment used to create inverted repeat in RNAi construct from the Vienna Drosophila RNAi Center (Dickson B. et al. 2007.7.18). "GD" identifer also used for allele and construct symbols.
VDRC-1 Dataset Report
VDRC-2 Dataset Report.
TRiP RNAi amplicons
Extents of the amplicons are indicated with an orange bar.
FBlc0000048 TRiP-1 Dataset Report
FBlc0000153 TRiP-2 Dataset Report
FBlc0000185 TRiP-3 Dataset Report
FBlc0000186 TRiP-4 Dataset Report
FBlc0000416 TRiP-5 Dataset Report
BKNA RNAi amplicons
Extents of the amplicons are indicated with an orange bar.
HD2 Dataset Report (dsRNA amplicon platform) RNAi amplicons from the GenomeRNAi database.
HFA RNAi amplicons
Extents of the amplicons are indicated with an orange bar.
HFA Datset Report.
NIG-Fly RNAi amplicons
Extents of the amplicons are indicated with an orange bar.
NIG_RNAi_Fly-1 Datset Report.
sgRNA Reagents
TRiP-OE sgRNAs (overexpression)
Genomic sequences used as short guide RNAs in UAS constructs designed to target genes for CRISPR/Cas9-VPR-based overexpression. Extents of sgRNAs are indicated by red glyphs (arrows indicate orientation). Two nearby sgRNAs are used in a single construct to target the upstream region of a given gene.
Example region: 2L:7305255..7308450
More information: TRiP-OE report
TRiP-KO sgRNAs (knockout)
Genomic sequences used as short guide RNAs in UAS constructs designed to target genes for CRISPR/Cas9-based mutation. Extents of sgRNAs are indicated by red glyphs (arrows indicate orientation).
Example region: 2R:16654718..16655037
More information: TRiP-KO report
Predicted sgRNAs
Sequences predicted to be suitable as sgRNAs for genome engineering. These comprise all possible 23-mers in the D. melanogaster Release6 genome assembly that have 1) a 3-prime PAM sequence (NGG) and 2) a 15 bp sequence that is unique to the genome (including the PAM sequence). The seed score for each sgRNA, which ranges from 12 to 15 bases, indicates the uniqueness of the base pairing end of the sgRNA (excluding the PAM sequence). The frameshift score is the percent of frameshift changes predicted by micro-homology around the target site; the higher the score, the better suited the sgRNA for knockout. Because base pair mismatches can be tolerated outside the seed region, predicted sgRNAs were evaluated for potential off-target sites allowing for 3, 4 or 5 mismatches; potential sgRNA sequences are sorted into five browser tracks based on their predicted specificity at different stringencies.
Example region: 2L:7314441..7314673
More information: DRSC_sgRNA_designs report
Other Reagents
Putative brain enhancers (Pfeiffer et al.) GMR_Brain_exp_1 Dataset Report. Glyphs represent putative enhancers used to generate fly stocks carrying GAL4 transgenic constructs designed to be expressed in adult brain. Stocks are available from the Bloomington Stock Center. Clicking the glyph brings up the associated Sequence Feature report (e.g. http://flybase.org/reports/FBsf0000162377.html). On the Sequence Feature report, under "associated information" there is a construct listed. Clicking this construct link brings up the associated Construct Report (e.g. http://flybase.org/reports/FBtp0058072.html) on which you can find a link to the Stock Report (e.g. http://flybase.org/reports/FBst0045107.html). Sorry it's so roundabout!
VDRC Vienna Tiles GAL4 lines VDRC-VT Dataset Report. Glyphs represent putative enhancers used to generate fly stocks carrying GAL4 transgenic constructs. Stocks are available from the Vienna Drosophila Resource Center. Clicking the glyph brings up the associated Sequence Feature report (e.g. VT020839), with links to the related stock reports.
Tiling BACs Tiling BAC indicated by narrow gray bar. BAC genomic clones used by the Berkeley Drosophila Genome Project as part of the minimal tiling path used for determination of the D. melanogaster genomic sequence (Celniker SE. et al. 2002).
Pacman Chori-321_BAC CHORI-321_BAC Dataset Report. The blue glyphs indicate the extent of the BAC, inferred from the mapping of the sequenced BAC insert ends; CHORI-321 BAC inserts are, on average, 83 kbp in size.
Pacman Chori-322_BAC CHORI-322_BAC Dataset Report. The blue glyphs indicate the extent of the BAC, inferred from the mapping of the sequenced BAC insert ends; CHORI-322 BAC inserts are, on average, 21 kbp in size.
BLAST Hit
BLAST HSP If entry into GBrowse was via a linked hit using the FlyBase BLAST tool, the extent of the aligned region is shown as a vertical grey bar that extends through all the GBrowse tiers.
Analysis
Restriction Sites Clicking here marks cut sites for the common restriction enzymes PvuII, ClaI, BamHI, EcoRI.